A group of scientists has developed a novel category of titanium alloys that possess high strength and resilience when subjected to tension, utilising a combination of alloy composition and 3D-printing technologies.
The achievement, documented in the journal Nature, has the potential to expand the use of titanium alloys, enhance sustainability, and inspire advancements in alloy design. This discovery opens up possibilities for the development of a fresh category of eco-friendly, high-performance titanium alloys, applicable in a wide range of fields including aerospace, biomedical, chemical engineering, space exploration, and energy technologies.
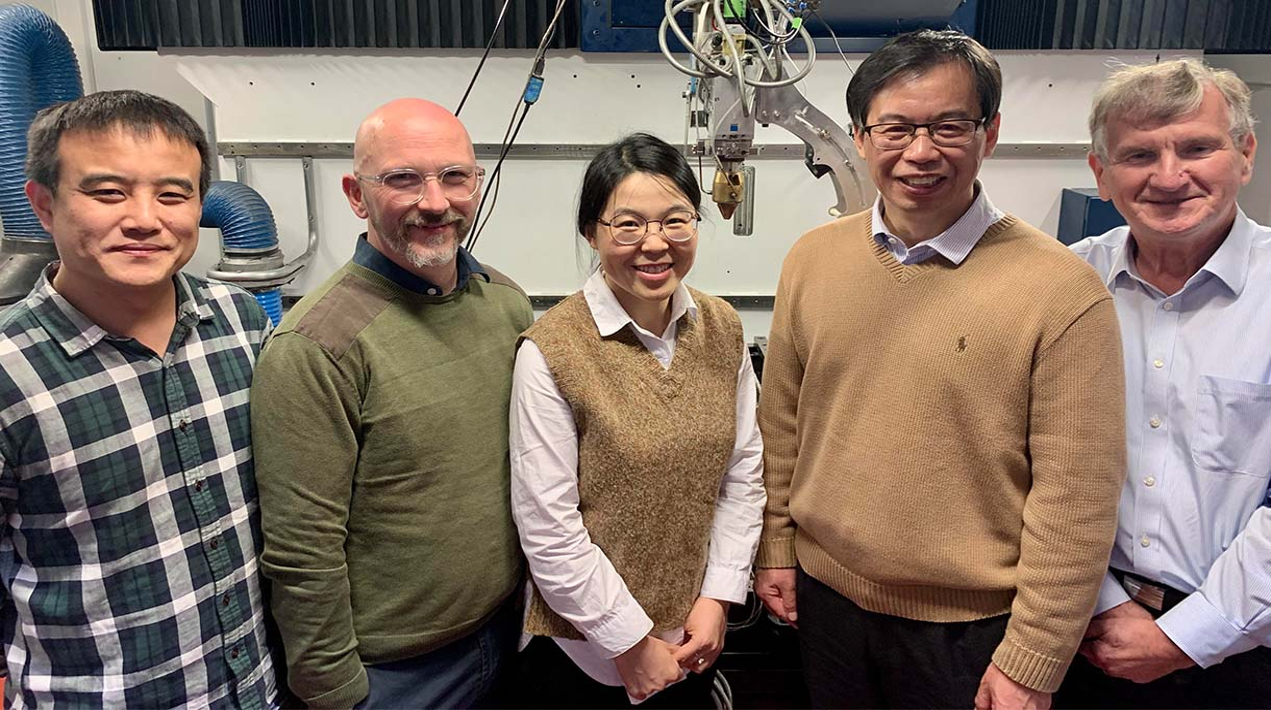
The innovation was spearheaded by RMIT University and the University of Sydney, in collaboration with Hong Kong Polytechnic University and Melbourne-based company Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence. These institutions and industry partners joined forces to drive this remarkable advancement in titanium alloy research.
The team’s lead researcher, Distinguished Professor Ma Qian from RMIT, emphasised the incorporation of circular economy principles into their design, presenting a significant opportunity to manufacture the new titanium alloys from industrial waste and low-grade materials.
Professor Qian, based at RMIT’s Centre for Additive Manufacturing in the School of Engineering, expressed that utilising waste and lower-quality resources has the potential to generate economic value and mitigate the substantial carbon footprint associated with the titanium industry.
The titanium alloys developed by the research team are composed of a combination of two types of titanium crystals: the alpha-titanium phase and the beta-titanium phase. These phases correspond to distinct atomic arrangements within the material.
This particular class of alloys has been the fundamental building block of the titanium industry for many years. Traditionally, since 1954, these alloys have been created by incorporating aluminium and vanadium into titanium.
The team of researchers focused on exploring the potential of utilising oxygen and iron as stabilisers and enhancers for the alpha- and beta-titanium phases. Oxygen and iron are both readily available and cost-effective, making them highly attractive options for this purpose.
The development of robust and malleable alpha-beta titanium-oxygen-iron alloys has faced two major obstacles when using traditional manufacturing methods.
The first challenge is the adverse effect of oxygen on titanium, which can render it brittle. The second challenge arises from the addition of iron, which may result in significant defects in the form of large beta-titanium patches.
To overcome these challenges, the research team employed Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED), a 3D printing technique suitable for fabricating intricate and sizable components. By using metal powder, they successfully printed their alloys, effectively addressing the limitations associated with conventional manufacturing processes.
The successful outcome was made possible by integrating the team’s alloy design concepts with the design of the 3D-printing process. This combination allowed them to identify a range of alloys that exhibit remarkable strength, ductility, and ease of printing.
The team attributes the excellent properties of these new alloys, which can rival those of commercial alloys, to their unique microstructure.
Co-lead researcher Professor Simon Ringer, Pro-Vice-Chancellor at the University of Sydney, highlighted the significance of this research. He stated that the development of this new titanium alloy system offers a wide and adjustable range of mechanical properties, high manufacturability, and immense potential for reducing emissions. Additionally, it provides insights into materials design for similar systems.
The key element behind the success of these alloys is the distinct distribution of oxygen and iron atoms within and between the alpha-titanium and beta-titanium phases. The researchers engineered a nanoscale gradient of oxygen within the alpha-titanium phase, comprising sections with high oxygen content that exhibit strength, and sections with low oxygen content that demonstrate ductility. This control over local atomic bonding helps mitigate the risk of embrittlement.
The team is embarking on a significant journey, transitioning from proving their new concepts to pursuing industrial applications. The potential and advantages of 3D printing as a revolutionary method for producing innovative alloys. Moreover, the opportunity for the industry to use waste materials, such as sponge titanium-oxygen-iron alloy and recycled high-oxygen titanium powders, through their approach.
The insights gained from this work could serve as a template for mitigating oxygen embrittlement challenges in various metals and their alloys, including zirconium, niobium, and molybdenum, through 3D printing and microstructure design.
The research was made possible due to continuous and focused investments in research infrastructure by national and state governments, as well as universities. He emphasised that this work demonstrates the effectiveness of Australia’s national collaborative research infrastructure strategy and sets the stage for its expansion into advanced manufacturing.
The research conducted by the team received funding and support from several sources. The Australia Research Council (ARC) contributed through the Discovery Program and the Training Centre in Surface Engineering for Advanced Materials (SEAM). Additionally, support was received from the Australia-US Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative program, which is backed by the Australian Government.
The team also expressed their gratitude to The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and the State Key Laboratories in Hong Kong, funded by the Innovation and Technology Commission of the Government.